Skin Cancer
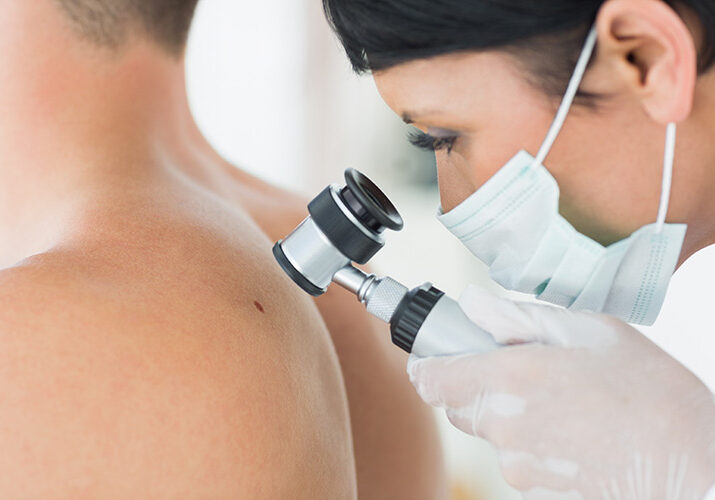
ABOUT Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a growth of abnormal cells in skin caused by unrepaired DNA damage that triggers mutations. These mutations lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors.
The three most common types of skin cancer are:
Basal Cell Carcinoma: This is the most common type of skin cancer that usually occurs in areas with significant sun exposure. It doesn't generally travel to other parts of the body, but can be very locally destructive.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): The second most common skin cancer, SCC is also heavily affected by sun exposure. This cancer can grow rapidly and can travel to other areas eventually if not addressed appropriately.
Melanoma: This type of skin cancer usually starts on the skin, however can travel to other parts of the body over time. It originates from the pigment-producing cells of the skin and is often affected by sun exposure, but can also occur in areas that are covered.
Skin Cancer Detection
The prevention of skin cancer starts with knowing your ABCDEs and being aware of your melanoma family history. ABCDE is an acronym that can help you remember what to look for on your skin.
"A" FOR
ASYMMETRY
"A" FOR ASYMMETRY
Look for moles or pigmented spots
where one half is unlike the other.
"B" FOR
BORDERS
"B" IS FOR BORDERS
irregular, scalloped or poorly circumscribed borders.
"C" FOR
COLOR
"C" IS FOR COLOR
If color is varied from one area to another, this is possibly a reason for concern.
"D" FOR
DIAMETER
"D" IS FOR DIAMETER
while melanomas are usually greater than 6mm in diameter when diagnosed, they can be smaller.
"E" FOR
EVOLVING
"E" IS FOR EVOLVING
If you notice a mole changing over time —changes in size or structure, itches, or bleeds.
SKIN CANCER TREATMENT
Your treatment options for skin cancer will vary, depending on the size, type, depth and location of the lesions. Small skin cancers may be fully removed in the initial biopsy
If additional treatment is needed, options may include:
- Excisional surgery
- Mohs surgery
- Curettage and electrodesiccation or cryotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Photodynamic therapy
- Immunotherapy
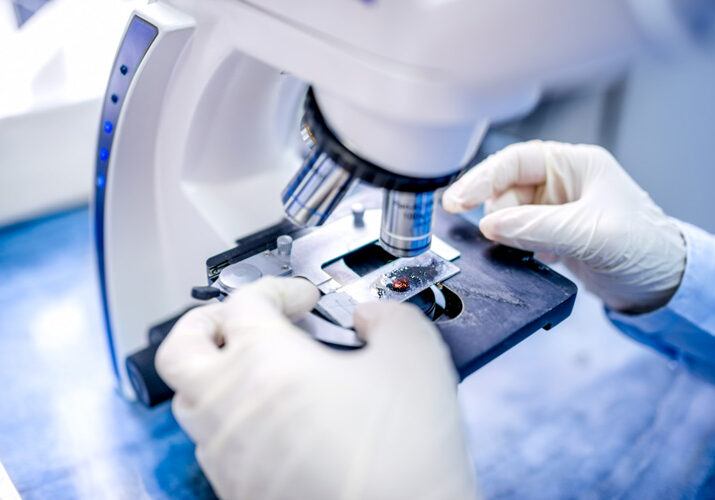
Mohs Micrographic surgery
Mohs surgery is a precise, outpatient procedure to remove high-risk skin cancer while preserving healthy tissue. The process of microscopic examination and layer-by-layer excision allows for complete tumor removal and high cure rates.
This state-of-the-art procedure allows our board-certified Mohs surgeons to see beyond the visible disease. At Core Dermatology, we are proud to offer this highly effective skin cancer treatment.
